实践 Vue3 组件库-基于 VuePress 开发组件文档
这篇我们来搭建一个文档系统,文档系统有很多选择比如 storybook、vuepress、vitepress 或者自建文档。这里选择基于 vuepress 搭建,因为 vuepress 功能完善也容易扩展。后续也会有单独基于 vitepress 的文档系统。
接下来我们就基于 vuepress 搭建文件,并自己实现一个组件演示的插件。本篇新增的完整代码可查看单独的分支 2-docs。也顺便推荐我提取出来的用于组件开发场景的 VuePress 的插件 vmi,实现了接近于 dumi 的体验和功能。
如果你还不了解这个系列要做什么,那你可以先阅读 【实践 Vue3 组件库-介绍一下这个系列】 的介绍,以便你对整个系列有清晰的认识。
版本问题
无论是 vuepress 还是 vitepress 都没有发布正式版本,它们在每个版本里都会有些破坏性更新。而 vuepress 最近也是将要全部迁移到了 Pure ESM 现在还不稳定。所以本篇文章全部基于 2.0.0-beta.49 版本,如果你需要更新可以查看 CHANGELOG 的变更记录。
文档结构
先根据 VuePress 的文档在根目录下新建 docs 目录把基础的结构搭建完成。
# 工具包
pnpm add vue rimraf anywhere -D --filter @bfehub/docs
# VuePress 依赖
pnpm add vuepress@2.0.0-beta.49 @vuepress/client@2.0.0-beta.49 -D --filter @bfehub/docs
新建一个 config.ts 添加一些默认的配置。
// docs/.vuepress/config.ts
import { defineUserConfig, defaultTheme } from "vuepress";
import { viteBundler } from "@vuepress/bundler-vite";
export default defineUserConfig({
base: "/vlib-starter/",
locales: {
"/": {
lang: "zh-CN",
title: "vlib-starter",
description: "Vue3 组件库开发模板 & Vue3 组件库实践指南",
},
},
bundler: viteBundler({
viteOptions: {},
vuePluginOptions: {},
}),
theme: defaultTheme({
locales: {
"/": {
navbar: [],
sidebar: {},
selectLanguageName: "简体中文",
selectLanguageText: "选择语言",
selectLanguageAriaLabel: "选择语言",
},
},
}),
});
再补充完善一些其他的配置,得到一个如下的结构。
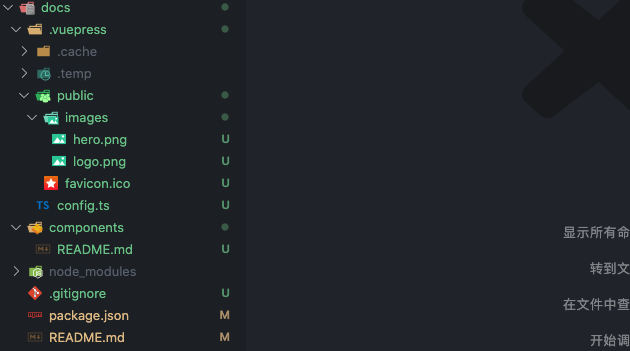
扩展页面
默认情况下 VuePress 只抓取源目录的文件(docs),但是我们设计的文档和组件是放在一起的在 packages/vlib-ui/src 下各个组件内,这时我们改怎么处理?
首先更改 pagePatterns 配置,把组件的文档包含在内。
// docs/.vuepress/config.ts
export default defineUserConfig({
pagePatterns: [
"**/*.md",
"!.vuepress",
"!node_modules",
// 查找组件的文件
"../packages/vlib-ui/**/*.md",
"!../packages/**/node_modules",
],
});
那我们在配置侧边栏的时候就要这样去写。
import type { SidebarConfig } from "vuepress";
export const zh: SidebarConfig = {
"/components": [
{
text: "基础组件",
children: [
{
text: "Button 按钮",
link: "/components/button/",
},
],
},
],
};
为了使页面路由访问正常,还需要利用 permalink 的特性,在文档页面手动自定页面访问路径。
---
permalink: /components/button
---
<!-- packages/vlib-ui/src/button/README.md -->
# button
这里我们启动文档服务即可访问到我们在 packages/vlib-ui/src/button/README.md 中写的文档。
组件演示
我们需要给文档添加组件演示的功能,你也可以使用社区现有的插件如之前提到的 vmi。如果为了便于扩展也可以自己开发。接下来我们就开发一个这样的插件,先定义期望的用法和语法。
所有的组件 demo 都放在 __demos__ 目录下,使用单文件的方式编写可以有更好的代码规范。
<!-- packages/vlib-ui/src/button/__demos__/basic.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<button>按钮一</button>
<button>按钮二</button>
</div>
</template>
在文档中自定义一个标签引入。
<!-- packages/vlib-ui/src/button/README.md -->
<demo src="./__demos__/basic.vue"></demo>
我们继续在 packages 创建一个 vuepress-plugins 子文件夹。包名称为 @bfehub/vuepress-plugins,并安装相关依赖。
// packages/vuepress-plugins/package.json
{
"name": "@bfehub/vuepress-plugins",
"private": true,
"main": "index.ts",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Vuepress Plugins."
}
# 前置依赖
pnpm add vue vite -D --filter @bfehub/vuepress-plugins
# 核心开发工具包
pnpm add @vuepress/core@2.0.0-beta.49 @vuepress/client@2.0.0-beta.49 @vuepress/utils@2.0.0-beta.49 --filter @bfehub/vuepress-plugins
# 解析 markdown 语法工具包
pnpm add @vuepress/markdown@2.0.0-beta.49 @vuepress/plugin-prismjs@2.0.0-beta.49 --filter @bfehub/vuepress-plugins
# 解析标签(<demo></demo>)语法工具包
pnpm add posthtml-parser posthtml-render --filter @bfehub/vuepress-plugins
# 客户端开发工具包
pnpm add @vueuse/core --filter @bfehub/vuepress-plugins
开发插件
一个 VuePress 插件一般为分两部分:一部分是 node 端用来解析 markdown 语法、读取文件控制最终生成的文件内容。一部分是 client 端用来处理组件最终展示的效果。可以访问 架构 部分的文档了解更多。
现在在 vuepress-plugins 下创建如下的结构,文件的内容分别如下。
├── code-block
│ ├── client
│ │ └── clientConfig.ts
│ ├── node
│ │ └── index.ts
│ ├── index.ts
└── index.ts
// packages/vuepress-plugins/code-block/client/clientConfig.ts
import { defineClientConfig } from "@vuepress/client";
export default defineClientConfig({
enhance(app) {
console.log("clientConfig", app);
},
});
// packages/vuepress-plugins/code-block/index.ts
import { path } from "@vuepress/utils";
export const codeBlockPlugin = () => {
return {
name: "@bfehub/vuepress-plugin-code-block",
clientConfigFile: path.resolve(__dirname, "./client/clientConfig.ts"),
};
};
// packages/vuepress-plugins/index.ts
export * from "./code-block";
这样就开发一个一个基础的插件虽然没功能,在自身项目中使用它。
pnpm add @bfehub/vuepress-plugins -D --filter @bfehub/docs
// docs/.vuepress/config.ts
import { defineUserConfig } from "vuepress";
import { codeBlockPlugin } from "@bfehub/vuepress-plugins";
export default defineUserConfig({
// ...
plugins: [
// @bfehub/vuepress-plugins
codeBlockPlugin(),
],
});
这时再访问文档服务查看页面控制台会打印出 clientConfig 证明插件就生效了。
服务端开发
VuePress 使用 markdown-it 来解析 Markdown 内容,因此可以借助于 markdown-it 插件来实现语法扩展。如果你不熟悉 markdown-it 的解析语法你可以阅读 冴羽大佬的系列文章
VuePress 暴露了 extendsMarkdown 用于我们扩展 Markdown 语法。
先整理以下开发思路:
使用 markdown-it 插件解析新增的 markdown 语法,查找到
demo标签。使用 posthtml-parser 解析
demo的标签src属性(使用这个包是为了方便扩展解析)。根据
src属性读取到demo的 文件路径 用于当前文档页面需要加载的组件,文件内容 用于我们的高亮代码和原始代码。把当前文档中解析到
demo信息以文档路径存储起来,在最终文件生成的时候添加进去。
先使用插件的 extendsMarkdown 扩展来开发一个 resolveHtmlBlock 的语法解析插件。
// packages/vuepress-plugins/code-block/index.ts
import { path } from "@vuepress/utils";
import { resolveHtmlBlock } from "./node";
export const codeBlockPlugin = () => {
// 存储当前的文档页面引入了哪些 demo 组件
const store = new Map<string, Set<string>>();
return {
name: "@bfehub/vuepress-plugin-code-block",
clientConfigFile: path.resolve(__dirname, "./client/clientConfig.ts"),
// 扩展 markdown
extendsMarkdown(md) {
resolveHtmlBlock(md, store);
},
};
};
在 resolveHtmlBlock 方法中扩展 markdown-it 的 html_block 的渲染规则,判断当前的 token 是不是我们定义的 demo 标签,如果是解析并覆盖当前的 token 内容。
// packages/vuepress-plugins/code-block/node/resolveHtmlBlock.ts
import type { Markdown, MarkdownEnv } from "@vuepress/markdown";
import { parseCodeBlock } from ".";
export function resolveHtmlBlock(md: Markdown, store: Map<string, Set<string>>) {
const rawRule = md.renderer.rules.html_block!;
// 扩展 html_block 渲染规则,保存原始的渲染规则处理完后再调用原始的渲染规则。
md.renderer.rules.html_block = function (tokens, idx, opts, env: MarkdownEnv, self) {
const content = tokens[idx].content;
// 判断当前 token 是否是我们需要的
if (content.startsWith(`<demo`)) {
tokens[idx].content = parseCodeBlock(store, content, env.filePath!);
}
return rawRule(tokens, idx, opts, env, self);
};
}
在 parseCodeBlock 中解析标签的属性、存储到缓存、读取文件内容等一系列操作后,返回最终的 html 片段就是我们需要需要渲染的。
// packages/vuepress-plugins/code-block/node/parseCodeBlock.ts
import { path } from "@vuepress/utils";
import { type Node, parser } from "posthtml-parser";
import { render } from "posthtml-render";
import { readSource } from ".";
export function parseCodeBlock(
store: Map<string, Set<string>>,
content: string,
pagePath: string
): string {
const html: Node[] = parser(content);
let i = -1;
for (const node of html) {
i++;
if (typeof node !== "object") {
continue;
}
if (node.tag !== "demo") {
continue;
}
if (typeof node.attrs?.src !== "string") {
continue;
}
// 当前页面引用的外部添加进缓存,页面扩展时使用
const dirPath = path.dirname(pagePath);
const compPath = path.resolve(dirPath, node.attrs?.src);
if (!store.has(pagePath)) store.set(pagePath, new Set());
store.get(pagePath)?.add(compPath);
// 读取文件,生成新的标签结构。
// tag: 节点的名称,在 vue 文件中是组件名。
// attrs: 节点的属性,在 vue 文件中是 props 属性。
// content: 子节点,在 vue 文件中用 slot 渲染。
const source = readSource(compPath);
html[i] = {
tag: "VlibDemo",
attrs: {
name: source.name,
rawCode: encodeURIComponent(source.rawCode),
highlightCode: encodeURIComponent(source.highlightCode),
},
content: [
{
tag: `VlibDemo${store.get(pagePath)?.size}`,
},
],
};
}
return render(html);
}
读取文件单独提取出了 readSource 文件,在这个函数我们实现读取文件内容和高亮文件内容。
import { fs, path, warn } from "@vuepress/utils";
import { createMarkdown } from "@vuepress/markdown";
import { resolveHighlighter } from "@vuepress/plugin-prismjs";
export function readSource(filePath: string) {
let code = "";
const name = path.basename(filePath);
const lang = path.extname(name).slice(1);
if (fs.existsSync(filePath)) {
code = fs.readFileSync(filePath, "utf-8");
} else {
warn("找不到文件:" + path);
}
return {
name,
rawCode: code,
highlightCode: createMarkdown({
highlight: resolveHighlighter(lang),
}).render("```" + lang + "\n" + code + "```"),
};
}
这时服务端部分就开发完毕。我们回到页面上看到已经渲染出来了,因为 VlibDemo 和 VlibDemo1 还不是 Vue 组件所以无法渲染。

客户端开发
客户端部分我们需要开发一个全局的 VlibDemo 组件。有两个主要的点:一个是 slot 对应 content 的内容;一个是 props 对应 attrs 的属性。这两部分放在那和怎么使用都可以自由发挥了。
下面部分是简单的写的,涉及到的样式和图标就不单独放出来了可以去源码中复制。
<!-- packages/vuepress-plugins/code-block/client/components/demo.vue -->
<template>
<div class="vlib-demo">
<div class="vlib-demo-example">
<ClientOnly>
<slot>渲染 content 内容</slot>
</ClientOnly>
</div>
<div class="vlib-demo-content">
<div class="vlib-demo-action">
<span class="vlib-demo-action-button" @click="handleCopy">
<Copy v-show="!state.isCopy" />
<CopySuccess v-show="state.isCopy" />
</span>
<span>{{ props.name }}</span>
<span class="vlib-demo-action-button" @click="handleExpand">
<Expand v-show="!state.isExpand" />
<UnExpand v-show="state.isExpand" />
</span>
</div>
<div
v-show="state.isExpand"
class="vlib-demo-source"
v-html="decodeURIComponent(props.highlightCode)"
></div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { ref, reactive } from "vue";
import { useClipboard } from "@vueuse/core";
import Expand from "../icons/Expand.vue";
import UnExpand from "../icons/UnExpand.vue";
import Copy from "../icons/Copy.vue";
import CopySuccess from "../icons/CopySuccess.vue";
const props = defineProps<{
name: string;
rawCode: string;
highlightCode: string;
}>();
/**
* Code status
*/
const state = reactive({
active: 0,
isCopy: false,
isExpand: false,
});
const handleExpand = () => {
state.isExpand = !state.isExpand;
};
/**
* Copy raw code
*/
const rawCode = ref("");
const { copy } = useClipboard({ source: rawCode });
const handleCopy = async () => {
rawCode.value = decodeURIComponent(props.rawCode);
await copy();
state.isCopy = true;
setTimeout(() => {
state.isCopy = false;
}, 1000);
};
</script>
之后把 VlibDemo 注册到全局组件中。
// packages/vuepress-plugins/code-block/client/clientConfig.ts
import { defineClientConfig } from "@vuepress/client";
import Demo from "./components/demo.vue";
import "./styles/index.scss";
export default defineClientConfig({
enhance({ app }) {
app.component("VlibDemo", Demo);
},
});
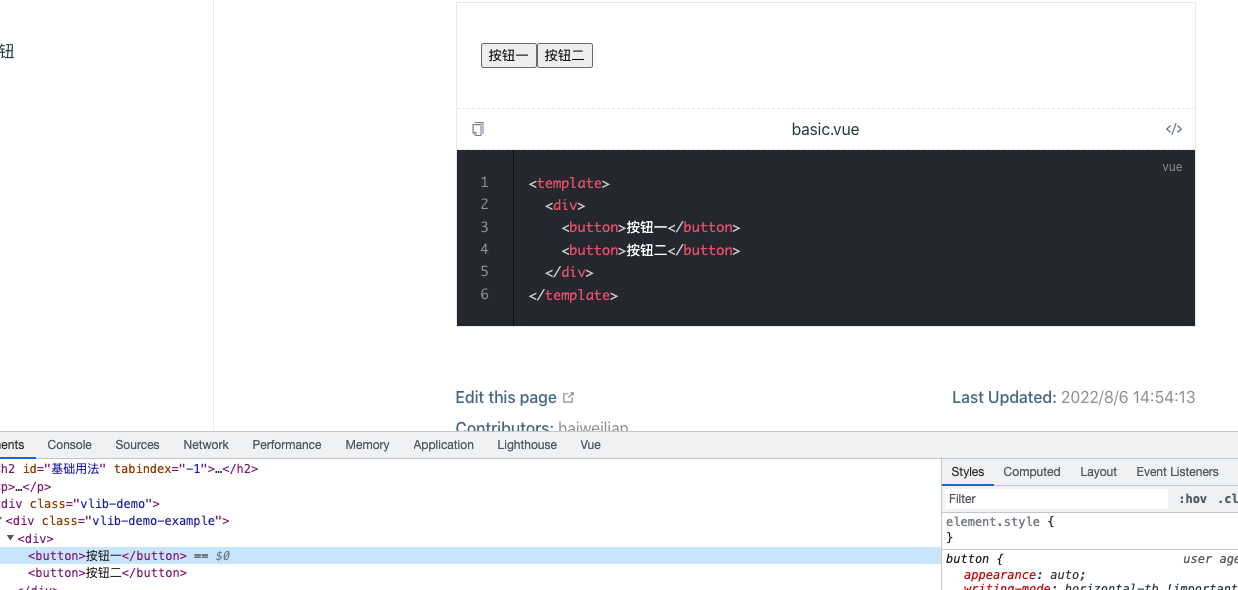
这是我们再看文档已经展示基本的效果了。
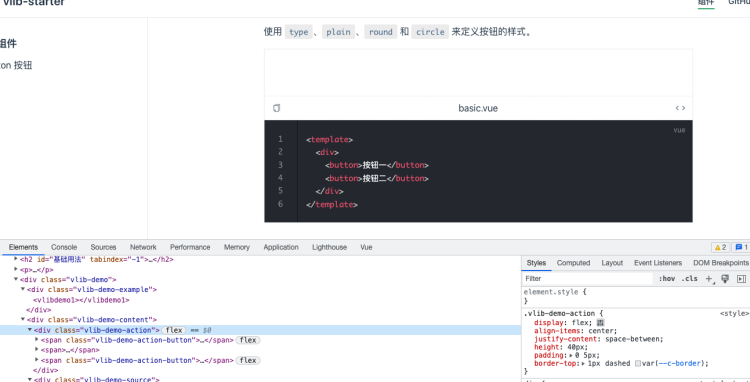
但是 VlibDemo1 这个组件没有解析处理。这就要使用 extendsPage 和 sfcBlocks 在文档页面引入所需要 demo 组件。
由于在服务端的时候我们存储过缓存了,所以可以直接读取到。
// packages/vuepress-plugins/code-block/index.ts
import { resolveHtmlBlock, resolveScriptSetup } from "./node";
export const codeBlockPlugin = (): Plugin => {
const store = new Map<string, Set<string>>();
return {
//...
extendsPage(page) {
resolveScriptSetup(page, store);
},
};
};
// packages/vuepress-plugins/code-block/node/resolveScriptSetup.ts
import type { Page } from "@vuepress/core";
const scriptRegExp = /<script\s(.*\s)?setup(\s.*)?>([\s\S]*)<\/script>/;
export const resolveScriptSetup = (page: Page, store: Map<string, Set<string>>) => {
const deps = store.get(page.filePath!);
if (!deps) return;
let i = 0;
let original = "";
// 如果在页面中写了 `script setup` 提取内容,往里追加组件导入的代码,在重写回去。
for (const tag of page.sfcBlocks) {
if (tag.trim().startsWith("<script")) {
original = tag.match(scriptRegExp)?.[3] ?? "";
break;
}
i++;
}
// 根据缓存中存储的组件路径导入组件,组件名称和生成节点时的规则一致。
page.sfcBlocks[i] = combineScriptSetup([...deps], original);
};
export const combineScriptSetup = (deps: string[], original: string) => {
return `\n
<script lang="ts" setup>
${deps.map((path, index) => `import VlibDemo${index + 1} from '${path}'`).join("\n")}
${original}\n
</script>\n`;
};
现在基本上完善了所有的功能了。
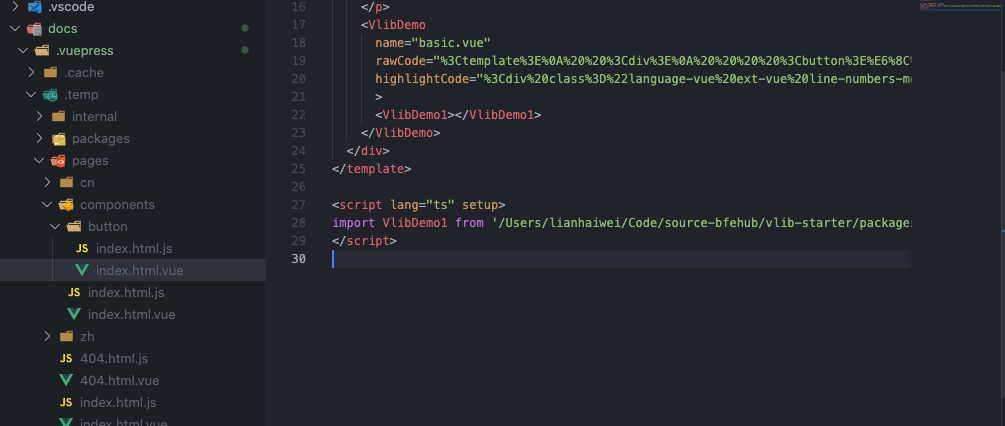
而最终生成的临时文件内容如下。
你可以...
你可以根据本章内容自己实现一遍完善我们的组件库。
你可以尝试把手写的永久链接开发一个插件自动生成。
你可以尝试开始说过的其他文档工具选择合适的。
如果对你有帮助可以点个 赞 和 关注 以示鼓励。
